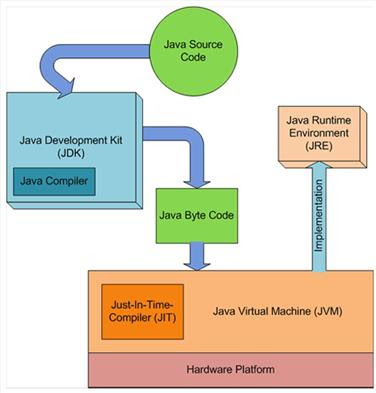
In Java you have to write and compile a program only once. The Java
on any platform will interpret the compiled bytecode into instructions
understandable by the particular processor. However java virtual machine
handles only one bytecode instruction at a time that makes execution
slow. But Using the Java just-in-time compiler at the particular system
platform compiles the bytecode into the particular system code. After
the code has been (re-)compiled by the JIT compiler, it will usually run
more quickly on the computer.
The just-in-time compiler comes with JVM and is used optionally. It compiles the bytecode into platform-specific executable code that is immediately executed. JIT compiler option should be used especially if the method executable is repeatedly reused in the code.
The just-in-time compiler comes with JVM and is used optionally. It compiles the bytecode into platform-specific executable code that is immediately executed. JIT compiler option should be used especially if the method executable is repeatedly reused in the code.